Financial Services
VAT Guide | VATGFS1
July 2019
Contents
1. Financial Services – Guidance Note
5. Input tax apportionment methods
Financial Services – Guidance Note
Overview
Short brief
VAT was introduced with effect from 1 January 2018 in the UAE. As a general consumption tax on the supply of goods and services, its effects must be understood by providers of financial services in the UAE, in two contexts:
Its application to the activities of all financial services providers; and
The approach financial services providers in the UAE should take to determine the amount of VAT on costs (i.e. input tax) they are eligible to reclaim where they make both taxable and exempt financial services.
Important : This document does not discuss insurance. This is covered in a separate Guide VATGIN1.
Purpose of this document
This document contains guidance about the characteristics of financial services for VAT purposes.
In addition, this document provides guidance for the financial services industry to understand which of the services and functions it provides are liable to and exempt from VAT and in turn, the extent to which VAT recovery on costs is possible. It explains the concept of input tax apportionment as well. Detail on Special Input Tax Apportionment Methods is provided in a separate Guide Input Tax Apportionment | VATGIT1.
Who should read this document?
This document should be read by those responsible for tax matters operating in the financial services industry in the UAE, as well as their tax agents and advisers.
It should be read in conjunction with the Taxable Person Guide for VATG001.
Status of the document
This guidance is not a legally binding statement, but is intended to provide assistance in understanding and applying the VAT legislation.
Financial Services
Financial services
What are financial services?
These are services which are provided by businesses or persons which in some way are connected with finance. Many such services will be directly related to money. This could mean dealings in money or its equivalent, or the provision of credit. It also includes more specialist types of finance (for example, hire-purchase or instalment credit finance) or more long-term finance, such as shares or loan stock.
Some financial services may not have this direct link with money (for example, equipment leasing). In addition, there is a wide range of associated services which have a less immediate link to money (for example, financial advice, trustee services and debt collection).
Other more peripheral activities include investment brokerage and the underwriting of securities.
Financial services typically comprise a complex series of transactions and the products offered by the sector are continually evolving, through innovation and technology. In addition, the means of remuneration for financial services can also be complex (for example, margin and spread).
Historically, transactions in the sector were complex to analyse and presented difficulties, both in identifying the supply chains and the values of the various supplies being made.
However, more recently, financial services have become more easily identifiable and measurable than in the past due to technological advancements and global developments in the manner in which transactions are conducted.
Accordingly, the starting point for the UAE VAT treatment of financial services is that VAT should be charged on financial services where it is practicable to do so.
Specifically, where fees or similar readily identifiable charges are made for the provision of a financial service as defined in the Federal Decree-Law [1] and Executive Regulations [2] , such fees will be liable to VAT at the standard rate.
Financial services – the VAT Law
What are financial services as defined by the Law?
As defined by the Law [3] and Executive Regulations [4] , financial services are services connected to dealings in money (or its equivalent) and the provision of credit and include, but are not limited to the following:
The exchange of currency, whether effected by the exchange of bank notes or coin, by crediting or debiting accounts, or otherwise;
The issue, payment, collection, or transfer of ownership of a cheque or letter of credit;
The issue, allotment, drawing, acceptance, endorsement, or transfer of ownership of a debt security [5] ;
The provision of any loan, advance or credit;
The renewal or variation of a debt security, equity security [6] , or credit contract;
The provision, taking, variation, or release of a guarantee, indemnity, security, or bond in respect of the performance of obligations under a cheque, credit, equity security, debt security, or in respect of the activities specified in items (2) to (5) above;
The operation of any current, deposit or savings account;
The provision or transfer of ownership of financial instruments such as derivatives, options, swaps, credit default swaps, and futures;
The payment or collection of any amount of interest, principal, dividend, or other amount whatever in respect of any debt security, equity security, credit or contract of life insurance;
Agreeing to do, or arranging, any of the activities specified in items (1) to (9) above, other than advising thereon.
VAT
What is a taxable supply?
Most business transactions involve supplies of goods or services.
A taxable supply is one where there is:
A supply of goods or services;
For consideration;
Supplied in the course of conducting business in the UAE;
By a VAT registered business (or a business that is obliged to be VAT registered).
Taxable supplies may either be subject to the standard rate or zero rate of VAT.
The term ‘taxable supply’ excludes exempt supplies and any supplies that are outside the scope of UAE VAT.
Standard rate
In general terms, where VAT is charged at the standard rate, businesses that are registered for VAT are able to recover the VAT they are charged by their suppliers on goods and services, subject to certain conditions. VAT which is incurred on purchases is known as ‘input tax’.
Zero rate
VAT is charged but at 0% on zero-rated supplies. Zero-rated supplies are treated as taxable supplies in all respects, including the right of the person making the supply to recover the VAT on their own business expenditure.
What is an exempt supply?
No VAT is charged on exempt supplies. As these supplies are not ‘taxable supplies’, the supplier cannot recover any of the VAT on expenses (input tax) directly incurred in making exempt supplies.
In addition, businesses which make supplies with a mixture of differing VAT liabilities will need to use a method of apportionment in respect of VAT incurred on general costs (i.e. input tax which is non-attributable to either taxable or exempt supplies).
Incurred VAT therefore may represent a large irrecoverable cost to businesses involved in making supplies which are wholly or partly exempt from VAT, such as those operating in the financial services sector.
As codified in the UAE Law and in conformity with its obligations under the GCC VAT Agreement, the UAE has taken a very narrow approach to the use of VAT exemption.
Thus, the UAE will tax the majority of transactions taking place in the country at the standard rate, whilst only a very limited number of exceptions to this general rule will be made. These exceptions will include some financial services, subject to certain conditions, as outlined below.
Multiple supplies versus single composite supplies
A business will make multiple supplies where it charges a single inclusive price for a number of separate supplies of goods or services. This is different from a single supply of a mixture of goods or services (known as a single composite supply) to which a single rate of tax applies.
These scenarios can apply to financial services which may be packaged or ‘bundled’ together where they would ordinarily be treated as separate services or in the opposite situation, where a single composite supply may be unbundled or artificially split into separate components.
Multiple supplies
Where you make a multiple supply, you must determine the correct amount of VAT to charge.
If you make supplies and the individual supplies are: | Then you should: |
Liable to VAT at the same rate | Calculate the tax that is due in the normal way. |
Not liable to VAT at the same rate | Work out the tax value of each supply in order to calculate how much tax is due. |
Where the individual supplies are not liable to VAT at the same rate, you must use a method of valuing each supply which is fair and reasonable. This could include using the cost of each element of the supply as a proxy for assigning a value to each component of the supply. The value of each supply must be disclosed to the customer.
For example, a finance company provides credit finance upon the sale of goods via instalment payments. It charges for the cost of the goods and makes a separately disclosed interest charge. The interest charge will be exempt and the sale of the goods subject to VAT. This is because the two amounts are separately identified and the products, namely the goods and the supply of credit are not interrelated.
Single composite supplies
Single composite supplies are one, single indivisible supply of a mixture of goods and/or services. The supply is treated as a single supply and is subject to VAT at one rate which is applied to the value of the supply as a whole. You must not use apportionment where you make a composite supply.
There will be a single composite supply where one or more elements of the supply comprise the principal component, with other elements being ancillary – i.e. not an aim in itself, but a means of better enjoying the principal component. The contractual nature and wider circumstances of such supplies will be taken into account.
In addition, there will be a single composite supply where there is a supply which has two or more elements which are so closely linked that they form a single supply and which it would be artificial or impossible to split.
Charging a single price is not determinative, but may suggest that there is a single service. However, where there are indications that the recipient intended to buy two distinct services, with different VAT liabilities, this could mean that the single price should be apportioned.
Single composite supplies will not be accepted as such, unless:
One price is charged and the prices of the different components of the supply are not separately identified or charged by the supplier; and
The consideration payable by the recipient of the services and/or goods would not be affected were the recipient only to purchase the principal component of the supply; and
All the components of the supply are supplied by a single supplier.
For example, as a promotional offer, a bank may offer a loan product at a particular rate of interest which includes giving a new tablet to customers in order to make the product more attractive. Any fees or prices are not separately identified. The tablet is considered ancillary to the principal supply of the loan product as it is not an aim in itself.
Financial services and VAT
The VAT treatment of financial services in the UAE
General principle
The general principle applicable is that financial services, as defined by the VAT Law and Executive Regulations, will be subject to VAT at the standard rate when they are supplied for an explicit fee, discount, commission, rebate or similar type of charge.
Standard-rated services
Supplies of financial services where an explicit fee, discount, commission, rebate or similar type of charge is made are subject to VAT at the standard rate of VAT (i.e. they are treated as taxable supplies) to the extent of the amount of that separately identifiable charge. VAT incurred on costs wholly attributable to the standard rated supply can be recovered in full.
Banking Examples
| Types of financial service | Examples of fees liable to standard rate VAT |
|---|---|
Operation of a bank account |
|
Money transfers |
|
Cash |
|
Mortgages (including commercial mortgages) |
|
Loans, advances or credit (including business loans) |
|
Investment banking |
|
Card-related services |
|
Currency exchange |
|
Provision of safe custody facilities |
|
A more detailed list of charges for specific financial services is set out at Appendix A.
Zero-rated services – investment grade precious metals
The supply of investment grade precious metals [7] is also subject to VAT at the zero rate.
VAT incurred on costs wholly attributable to a zero-rated supply can also be recovered in full.
Exemption
Financial services, insofar as they are remunerated by way of an implicit margin or spread (i.e. no explicit fee [8] is charged in respect of them) will be exempt from VAT (i.e. they are not treated as taxable supplies). Accordingly, this VAT treatment will also apply to interest payable in respect of borrowing.
VAT incurred on costs wholly attributable to the exempt supply cannot be recovered at all.
In all cases, the following classes of financial services shall be exempt from VAT:
The issue, allotment, or transfer of ownership of an equity security or a debt security;
The provision, or transfer of ownership, of a life insurance contract or the provision of re-insurance in respect of any such contract (more details on insurance is included in the Insurance Guide VATGIN1).
A detailed list of charges for specific financial services is set out at Appendix A.
Exported Services
The supply of financial services to a recipient established outside the GCC [9] (whether or not they would otherwise have been exempt where supplied in the GCC) will be zero-rated (i.e. they are treated as taxable supplies).
Supplies of financial services to a recipient established within the GCC Implementing States have the following VAT treatments:
Where the recipient is registered or registerable for VAT in the GCC state in which the financial service is received, the supply is outside the scope of UAE VAT and the recipient is liable to account for the reverse charge in the GCC member state in which the supply is received, at the prevailing rate of VAT applicable to that service in that state.
Input tax which is wholly attributable to such supplies is recoverable whether or not the supplies in question would have been exempt or taxable in the UAE.
Where the recipient is not registered nor registerable for VAT in the GCC state in which the financial service is received, the place of that supply will be the UAE. In such instances, the supply will have the normal UAE VAT liability and related VAT recovery.
Imported Services
Where services are received from outside the GCC, those services will be liable to VAT at the standard rate where the supplies would be standard-rated supplies were they to be made in the UAE.
In this scenario, the imported services will be subject to the reverse charge mechanism as if the importer had supplied these services to itself. The importing financial services institution must therefore account for the VAT incurred on the imported services.
It will also be entitled to claim for the input tax on such services, subject to the usual rules of recovery, including those of input tax apportionment (see below).
Recovery of Input Tax
VAT incurred on costs which is partly attributable to taxable supplies and also to exempt supplies of financial services must be apportioned; only that part which is reasonably attributable to the taxable supply can be recovered. The supplier in question must make use of an ‘input tax apportionment’ method in order to determine the amount of input tax which it may recover in such circumstances. Please refer to section 5 below for further guidance.
Islamic Finance – VAT Treatment
Principles
Any supply made under an Islamic financial arrangement [10] , which is certified as Shariah compliant, and which has the intention of and achieves effectively the same result as a non-Islamic financial product, shall be treated in such a way as to give an outcome for the purposes of the Law comparable to that which would be the case for its non-Islamic counterpart.
This is to ensure equality of VAT treatment between Islamic and non-Islamic finance products.
In determining the correct VAT treatment for Islamic finance products, the purpose, structure and pricing of the Islamic product will be considered.
Accordingly, in order to ascertain the VAT liability of an Islamic financial product, the following process should be followed.
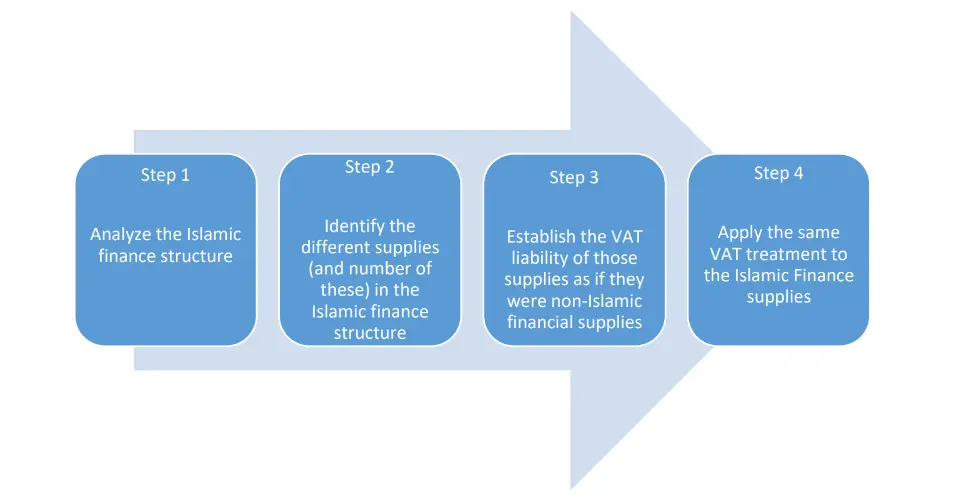
Example
For example, a commodity Murabaha entered into for lending purposes will be treated as a loan for VAT purposes. Any explicit fees will be taxable, unless the fees are only made explicit as a requirement of Shariah law and where their non-Islamic equivalents would also be treated as exempt.
Accordingly, the profit derived from the supply of the commodity on deferred payment terms would be exempt if this is used de facto as a loan and the non-Islamic equivalent consideration is interest.
Non-equivalent Products
It is recognised, however, that certain aspects of Islamic finance may preclude direct equivalence in VAT treatment being applied. In such cases, the underlying purpose, features and circumstances of the product concerned must be taken into account when determining the appropriate VAT treatment.
Any significant difference in the overall liability between an Islamic financial product and any non-Islamic counterpart arising as a consequence of differential treatment being applied will be addressed on a product-by-product basis.
Providers of particularly complex or non-standard Islamic financial products should analyse these carefully and consider seeking advice on the VAT liability of such products.
Other Financial Services – VAT Treatment
Returns on Investment
Where a financial service provider makes a payment which is a return on an investment, such as interest on deposits, dividends, drawings, etc., and where there is no service nor transaction provided in return for such a payment, then these returns on investment will be outside the scope of VAT.
Equity Securities and Debt Securities
The issue, allotment, or transfer of ownership of an equity security or a debt security will be exempt from VAT. This also includes stocks and other securities.
Fees charged by brokers or dealers who act as intermediaries to the above types of transactions will be subject to VAT at the standard rate.
Share registrar, trading, and settlement services which are provided in exchange for a fee, etc, will also be standard-rated. This includes fees charged for facilities provided by exchanges etc.
Where assistance is provided to a company with the management of shareholders and other financial stakeholders, payment of dividends, arranging annual general meetings and providing annual reports to shareholders, such services are standard-rated.
Portfolio Management
The management of a portfolio of investments is subject to VAT at the standard rate.
Trustee Services
Trustee services are subject to VAT at the standard rate.
Pensions and Collective Investments
Payments into a pension or a collective investment scheme are outside the scope of VAT. However, fees for the management of a pension fund or collective scheme are standard-rated.
Stock Lending
The lending of shares is not subject to VAT. However, if a fee is charged for this service, it will be subject to VAT at the standard rate.
Interest Rate Swaps
Where banks and financial institutions exchange fixed interest rates on their debts and there is no explicit fee for this service, this is exempt from VAT.
Currency Swaps
Where banks and financial institutions undertake currency swaps and there is no explicit fee for this service, this is exempt from VAT.
Other Derivatives
Derivatives are financial instruments whose price depends on the value of the underlying financial instrument, commodity, or currency to which the derivative relates.
Devising, advising on, originating, and issuing derivatives and similar structured products is liable to VAT at the standard rate, where this is carried out for an explicit fee (e.g., arranger’s fee, rollover fee, upfront fee). Where consideration is derived from an explicit premium, this is also standard-rated.
Trading in derivatives where income is derived from arbitrage or net margin or spread is exempt from VAT.
Trading income earned on the underlying financial instruments is also exempt.
The transfer of ownership of derivatives or of a future contract in relation to commodities, where there is no delivery of the underlying commodity, is exempt from VAT where carried out on a margin (i.e. non-explicit fee) basis.
However, settlement of futures contracts by delivery of commodities is taxable at the appropriate rate of VAT for the underlying supply of these commodities.
Intermediation Services
Services of intermediation are subject to VAT. For example, a financial advisor may act as intermediary in the arranging or sale of a financial product. Any fees or commissions they receive from either their customer or the financial service provider for their services are standard-rated.
Preparatory Services
Preparatory services that are carried out separately to and before a supply of a financial service, whether the financial service is exempt or taxable, are themselves standard-rated, for example, the preparation and delivery of data or undertaking a due diligence.
Debt Recovery and Litigation
Services related to debt recovery, litigation, and the management of the recovery of debts due from debtors are subject to VAT at the standard rate. This includes all services related to debt factoring.
Leasing
The hire or leasing of equipment is subject to VAT at the standard rate. Ownership of the equipment does not transfer to the lessee under this type of contract; rather, the contract grants the right to use the equipment for a specified period of time. Where equipment is subsequently sold to a third party at the end of the lease, this sale is also subject to VAT.
Hire Purchase, Credit Sales Agreements, etc.
The supply of credit is exempt from VAT (where there is no explicit fee etc.). However, if goods or services that are subject to VAT are supplied on credit, and the finance charge is included in the total amount payable by the buyer in instalments, then the total amount payable will be liable to VAT, as it will be subject to the same VAT treatment as the goods or services themselves. .
However, if separate charges of interest are made for the provision of the credit and these are not included in the charge for the goods, these interest charges will be exempt from VAT.
NB: This treatment will apply to any business which provides credit facilities of this type, e.g. retailers which have in-house credit providers or departments will be subject to this VAT treatment as well as banks or other financial service providers.
As noted above at section 4.1.2, explicit fees which are charged for the provision of credit, such as administration or set-up fees are subject to VAT at the standard rate.
Input tax apportionment methods
General approach for all methods
Fair and reasonable test
Input tax recovery must, in all cases reflect the actual use to which the VAT on the relevant cost has been put, or have been determined via an appropriate proxy (i.e. via an input tax apportionment method) for that use.
Whenever there is a requirement to apportion input tax which is partly attributable to different supplies, each of which carries a different right to recovery, there is an inherent risk that the means by which that apportionment is carried out and the results it renders are not necessarily representative of actual use.
In that regard, all businesses must take care when making use of an input tax apportionment method that it is ‘fair and reasonable’ in their particular circumstances. Where it is not, the business should take steps to ensure that an approved alternative method is identified and adopted. The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) will closely examine the results of input tax apportionment methods used by businesses as part of its normal compliance program and, where necessary, will intervene in order to ensure that a fair and reasonable outcome is secured.
Step 1: Direct attribution
In all cases, in each tax period all input tax which can be wholly attributed to any particular supply must be attributed to that supply and either recovered or blocked from recovery as appropriate. This is referred to as direct attribution.
Any input tax which cannot be wholly attributed in this manner must be apportioned by way of an input tax apportionment method in order to establish that part which may be recovered and that part which may not. A business may choose between either the standard input tax apportionment method (see step 2a below), or by application to and approval of the FTA a special input tax apportionment method (see step 2b below) in order to undertake the necessary apportionment.
It is accepted that whilst the standard method may reasonably apply to most businesses circumstances, this might not always be the case. Nevertheless, a business must only apply to the FTA to make use of a special input tax apportionment method where it has first established that the standard input tax apportionment method would not render a result which is fair and reasonable in the context of their particular circumstances.
Step 2a: Standard method - attribution of residual input tax
On a VAT monthly or quarterly basis (as applicable), all input tax that cannot be wholly attributed under step 1 (‘residual input tax’) is to be apportioned between taxable and exempt use in the following manner:
Determine the recovery ratio as a percentage[11]
Input tax wholly attributable to taxable supplies [12] in the VAT period concernedInput tax wholly attributable to supplies allowing VAT recovery in the period concerned and input tax that cannot be recovered in the tax period concerned
Apply the rounded recovery ratio percentage to the residual input tax:
Residual x Recovery Ratio % = Proportion of residual attributable to taxable supplies
Treat that proportion of the residual which is attributable to taxable supplies as recoverable in the normal manner (and include in the VAT return for the tax period in which the calculation was undertaken).
In the first period following the end of the previous tax year [13] , a calculation for the preceding VAT year should be carried out , using the same principles as above. This is known as the ‘annual adjustment’ and may lead to an increase or a decrease in the amount of input tax previously treated as recoverable on a quarterly basis under (3).
Furthermore, if there is a difference of more than AED 250,000 in any tax year between the recoverable input tax as calculated in accordance with the method described in this section and the input tax which would have been recoverable if the calculation was made on the basis of the actual use of the goods or services, then the taxable person should make an adjustment to the input tax in respect of the difference. The adjustment must be made in the first tax period following the end of the relevant tax year.
If the difference is less than AED 250,000, no adjustment is required to be made.
Step 2b: Special method - attribution of residual input tax
A business may, having first established that the standard input tax apportionment method is not appropriate for use in its particular circumstances, apply to the FTA to make use of a special input tax apportionment method. Each business making such an application to the FTA must provide details of the method which they intend to use and the reasons why the standard method is not otherwise appropriate.
Important: Written approval from the FTA must be obtained in advance of the use of any special method. In all cases approval for the use of a special input tax apportionment method will only be made on a prospective basis. An annual adjustment must also be carried out under all methods. Details of how to apply for a Special Method are provided in the Guide Input Tax Apportionment | VATGIT1.
Appendix A
Please note the VAT liability of fees outlined in this Appendix applies only when the Place of Supply for the financial services is in the UAE. Please also note the VAT liabilities stated below are general and that there may be transactions which fall outside of these general treatments which should be analysed on a case-by-case basis.
Retail and Private banking
Financial Service / Fee Type
VAT Liability
Notes
Fees for opening, maintaining, closing accounts, withdrawals, deposits, etc.
Standard rate
Early Redemption Fee
Standard rate
Transaction services fee
Standard rate
Minimum balance fee
Standard rate
Overdraft interest income charged to individual customers
Exempt
Overdraft fees
Standard rate
Dormant / inactivity account service charges
Standard rate
Extra fee to cover the additional cost of running a non-profitable account
Waiver of fee / services provided for free to all / or specific banking customers
Outside scope
For this type of charge to be outside scope, it must be clear that there is no consideration for a supply and it does not qualify as a deemed supply.
Fees for cheques, including issuance, cancellations, guarantees, copies, service charges, re-presenting dishonoured cheques, etc.
Standard rate
Certificate / letter issuance fees
Standard rate
Bank statement fees, etc.
Standard rate
Fees for traveller's cheques, foreign currency, etc.
Standard rate
Money transfer fees, including processing overdue payments
Standard rate
Fees for safe custody of cash
Standard rate
Direct debit / standing order fees, including re-presenting dishonoured amounts, etc.
Standard rate
Credit card membership fees, service charges, late payment fees, cash advance fees, over the limit fees, etc.
Standard rate
Interest income earned on credit cards
Exempt
Finance charge (Interest)
Exempt
Minimum spend fee
Standard rate
Dynamic currency conversion (forms part of the foreign exchange spread and implicit in nature)
Exempt
Earned on international transactions and is calculated by spread
Foreign exchange spreads earned on credit cards
Exempt
Issuance of loyalty points for use of card
Outside scope
This will only be outside scope if the points qualify as a "voucher" and the consideration received does not exceed the advertised face value. All contracts should be analysed in detail.
Redemption of loyalty points for use of card
Outside scope
Outside scope if there are no services received/provided by the financial institution, i.e. if the supply is between the merchant and the customer. All such contracts should be analysed in detail.
Cash rebate (award to customers)
Outside scope
Not a supply for VAT purposes
Cash back / profit sharing arrangement with selected merchants
Standard rate
Fee by bank for introducing business to the merchant
Fee and charges received by card brand companies
Standard rate
Debit cards - all related fees
Standard rate
Loan, mortgage and other credit facilities - all opening fees, processing fees, late payment fees, etc.
Standard rate
Delayed payment penal interest charges
Exempt
Implicit fee, as it is based on interest
Recovery of non-performing loans - all related fees
Standard rate
Hire purchase
Standard rate
Standard-rated as long as there is no implicit margin payment
Promissory notes
Standard rate
Gold loans (lending interest)
Exempt
Gold loans - transaction fees for gold certificates
Standard rate
Foreign Exchange (FX) - sales and purchase fees
Standard rate
FX realized profits and loss spot / translation (spread income)
Exempt
Company name change fees
Standard rate
Fees charged for name change of customers in bank systems
SMS services fee
Standard rate
Disbursements, e.g. collection of legal fees; cost recoveries (repossessions, irrecoverable tracing fee, auctioneer's commission, storage fees, towing fees, legal fees); sales agent fees, etc.
Outside scope
It is important that the services are supplied to the customer and not the financial institution for these to qualify as disbursements. All such contracts should be analysed in detail.
Settlement fees between banks
Standard rate
Correspondent Bank services
Standard rate
These will be standard-rated unless there is no consideration and it is merely a pass-through of the correspondent bank's fees.
Asset Management and Private banking
Fee Type/Activity
VAT Liability
Notes
Management fees, sales fees, distribution fees, performance fees, etc.
Standard rate
Revenue sharing arrangements - revenue share between Asset Management company and Private Banking Business Unit (two different entities and not part of the same Tax Group)
Standard rate
This is consideration for a supply.
Revenue share with third party companies on account of performance fee earned on funds
Standard rate
As above
Retrocessions / Rebates - commissions received from fund houses for routing customers for wealth-related transactions
Standard rate
Recharge income (e.g. recharges of expenses paid on behalf of underlying funds managed) – Disbursement
Outside scope
It is important that the services are supplied to the customer and not the financial institution for these to qualify as disbursements. All such contracts should be analysed in detail.
Custody and Securities Services, Trustees Services
Standard rate
Investment income – Interest income
Exempt
Initial investment by fund manager
Outside scope
Not a supply for VAT purposes
Commissions for switching, transfers, incentive fees, etc.
Standard rate
Equities trading
Fee Type/Activity
VAT Liability
Notes
Transaction fee income (Direct Fixed Income/Equities/FX)
Standard rate
Brokerage fees charged to customers
Standard rate
Interest received on fixed deposit placed with other banks
Exempt
Interest charged to or earned from customers on facility granted for margin trading
Exempt
Dividends received on investments
Outside scope
Not consideration for a supply for VAT purposes
Custody, processing fees, etc.
Standard rate
Operational losses borne by the business and not recharged to the customer
Outside scope
Not a supply for VAT purposes
Supply of underlying commodity
Standard rate, Zero rate, Exempt
Will be dependent on the type of contract and the form of consideration
Initial/variation margin – futures
Outside scope
Not consideration for a supply
Option Premiums over equity and debt securities
Exempt
These are specifically exempt; other option premiums are taxable as they are explicit fees for a service
Arrangement fees, rollover fees
Standard rate
Upfront fees premium for structured products
Standard rate
Early Redemption fee
Standard rate
Collection Fee in respect of Dividends, Interest, Coupons
Standard rate
Securities Lending fee
Standard rate
Manufactured dividends
Outside scope
Not a supply for VAT purposes
Manufactured interest
Exempt
Advisory services, e.g. retainer, milestone, and success fees
Standard rate
Clearing fees
Standard rate
Minimum Monthly Fees
Standard rate
Transaction banking
Fee Type/Activity
VAT Liability
Notes
Trade finance fees
Standard rate
Letter of Credit fees
Standard rate
Guarantee services fees
Standard rate
Corporate lending interest / profit which is akin to interest for Islamic loans
Exempt
Corporate lending all fees (e.g. settlement, termination, upfront fees, etc.)
Standard rate
Commission in lieu of exchange
Standard rate
Escrow fees
Standard rate
Salary and pension payments fees
Standard rate
Institutional banking
Fee Type/Activity
VAT Liability
Notes
Correspondent bank charges
Outside scope
It is important that the services are made by the correspondent bank to the customer and not by the financial institution in question for these to qualify as disbursements. Otherwise standard-rated.
Telex charges
Standard rate
Interest received from other banks
Exempt
Issue or transfer of debt securities
Exempt
Securitisation of debt security
Exempt
Transfer of a loan portfolio
Exempt
Transfer of debt security
Exempt
Sale of debts or receivables
Exempt
Assignment of debt with full recourse
Exempt
Asset finance lending component of instalments
Exempt
If interest
Interest adjustment
Exempt
Interest on late payment
Exempt
Interest subsidy from dealer/manufacturer
Exempt
Admin and all other fees
Standard rate
Principal component of instalments
Outside scope
Not a supply for VAT purposes
Corporate Finance/Investment banking
Fee Type/Activity
VAT Liability
Notes
Interest on loans
Exempt
All fee-based services
Standard rate
Treasury and Financial Markets
Fee Type/Activity
VAT Liability
Notes
All types of interest income
Exempt
Interbank Investment/Placement:
- Hibah received on Wadiah placement
Exempt
- Profits from Mudarabah Interbank Investments (MII) and commodity Murabaha placement
Exempt
Holding of Islamic Securities:
- Profits earned from holding of Islamic capital market instruments (IMTN, Sukuk, etc.)
Exempt
- Profits earned from holding of Islamic money market instruments (Islamic negotiable instruments, etc.)
Exempt
- Ta'widh (Late payment compensation)
Standard rate
Admin fee – the non-Islamic fee is also standard-rated
Trading gain on sales of Held-for-Trading (HFT) securities
Exempt
Trading gain on Bonds / Notes / Derivatives / Trading securities
Exempt
Trading as Principal Government Stock, Treasury Bills, Other Capital Market Transactions, Debentures, etc.
Exempt
Marked-to-Market gain on HFT securities
Outside scope
Not a supply for VAT purposes
Actual revaluation on investments
Outside scope
Market to market gains on derivatives / structured products
Outside scope
Capital gain on sale of Islamic securities
Exempt
Capital gain on sales of Available-for-Sales (AFS) securities
Exempt
Discount on Purchase of Fixed Income Instruments
Exempt
Dividend income on investments
Outside scope
Income from FX forwards, FX revaluations, market to market, etc.
Exempt
Capital gain on equity investments
Outside scope
Outside scope provided this is merely an accounting entry and consideration for a supply.
Issue of securities
Exempt
Supply of underlying physical commodity requiring physical delivery
Standard rate, Zero rate
Dependent on the type of commodity
Supply of a futures / forward / swap / option agreement, where there is no physical delivery of the underlying commodity
Exempt
Trading income earned on underlying securities
Exempt
Trading gains
Exempt
Full underwriting activity (where there is no explicit fee)
Exempt
Issuance or sale of bonds
Exempt
Redemption for the principal value
Outside scope
Arrangement fee for underwriting, purchase or sale of bonds
Standard rate
Managing the issue, placement, underwriting of new and existing securities
Standard rate
Handling charges for payment or collection of dividends, principal or interest in respect of securities
Standard rate
Fee for acting as receiving banker in connection with issue or placing of shares, stocks, etc.
Standard rate
Islamic finance
Fee Type/Activity
VAT Liability
Notes
Explicit fees (as per non-Islamic products)
Standard rate
Fees made in accordance with Shariah law and considered to be the equivalent of non-Islamic products
Exempt
Profit on deferred payment terms
Exempt
Late payment charges (paid to charity)
Standard rate
Taxable as explicit fees like this are taxable for non-Islamic products
Murabaha / Tawaruq - purchase and sale of supplies
Outside scope
Generally, outside scope unless the non-Islamic product would be taxable
- Commodity charges/fee
Standard rate
- Administration fee
Standard rate
Ijarah - purchase of assets by bank
Outside scope
Generally, outside scope unless the non-Islamic product would be taxable
- Principal component of instalments
Outside scope
- Administration fee
Standard rate
- Assessment fee
Standard rate
- Financing income (margin)
Exempt
This will be standard-rated if there is no credit charge in the non-Islamic equivalent (e.g. with some operating leases, etc.)
Mudaraba Arrangement fee
Standard rate
- Administration fee
Standard rate
- Commissions based on profit margin or other implicit margin
Exempt
- Profit margins
Exempt
Wakala - Management fee
Standard rate
- Administration fee
Standard rate
- Retention of excess profits
Exempt
- Profit margins
Exempt